
Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks Berkeley, published a paper entitled “ A Case for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks(RAID)”. Described the various types of Disk Arrays, referred to as the acronym RAID. The basic idea of RAID was to combine multiple, small inexpensive disks drive into an array of disk drives which yields performance
US5233618A Data correcting applicable to redundant
Redundant array of independent memory Wikipedia. RAID 0 4/3/2018 FTC YKM 5 •Data striped across n disks •Read/write in parallel •No redundancy. •Ex: 3 year disk reliability = 0.9 for 100% duty cycle. n = 14, The main Redundant Array of Inexpensive (or Independent) RAID types are listed below. RAID 0. RAID 0 makes it faster to read and write to the hard drives. But data redundancy is not available in RAID 0. If one of the disks of which the striped volume consists fails, then the entire volume fails. RAID 0 requires minimum two hard disks..
Synonyms for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks in Free Thesaurus. Antonyms for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks. 58 synonyms for raid: steal from, break into, loot, plunder, ransack, pillage, sack, attack, invade, assault, rifle, forage, fall upon, swoop down upon, reive. What are synonyms for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks? PDF The authors discuss various types of RAIDs (redundant arrays of inexpensive disks), a cost-effective option to meet the challenge of exponential growth in the processor and memory speeds.
then some disk in a 70-disk array will fail in (50,000 / 70) hours (roughly once a month!) Large arrays without redundancy too unreliable to be useful “Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks” (RAID) The redundant array of independent disks (RAID) is a philosophy of using multiple drives working as a single drive—an array—to provide speed or redundancy. There’s many different RAID levels and a good tech understand these levels and the benefits they provide.
Sep 03, 2014 · What is RAID? RAID – Redundant Array of Independent Disks September 3, 2014 Mukesh N Tekwani 2 3. Motivation for RAID Just as additional memory in form of cache, can improve system performance, in the same way additional disks can also improve … Methods and apparatus are provided for detecting and correcting various data errors that may arise in a mass data storage apparatus comprising a set of physical mass storage devices operating as one or more larger logical mass storage devices. A method and apparatus is provided for detecting and reconstructing incorrectly routed data. A method and apparatus is also provided for detecting when
• Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) - A storage system, not a file system Patterson, Katz, and Gibson (Berkeley, ’88) - Idea: Use many disks in parallel to increase storage bandwidth, improve reliability - Files are striped across disks - Each stripe portion is read/written in parallel - … Methods and apparatus are provided for detecting and correcting various data errors that may arise in a mass data storage apparatus comprising a set of physical mass storage devices operating as one or more larger logical mass storage devices. A method and apparatus is provided for detecting and reconstructing incorrectly routed data. A method and apparatus is also provided for detecting when
Twice as many disks are required to store the same data when compared to RAID 0. Array continues to operate so long as at least one drive is functioning. RAID 1 analysis Failure Rate: If Pr(disk fail) = 5%, then the probability of both the drives failing in a 2 disk array is P(both fail) = (0.05)2 = 0.25%. Twice as many disks are required to store the same data when compared to RAID 0. Array continues to operate so long as at least one drive is functioning. RAID 1 analysis Failure Rate: If Pr(disk fail) = 5%, then the probability of both the drives failing in a 2 disk array is P(both fail) = (0.05)2 = 0.25%.
New study on Industrial Growth of Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market 2019-2024: The global Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) market is comprehensively and Insightful information in the report, taking into consideration various factors such as competition, regional growth, segmentation, and Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market size by value and volume. Twice as many disks are required to store the same data when compared to RAID 0. Array continues to operate so long as at least one drive is functioning. RAID 1 analysis Failure Rate: If Pr(disk fail) = 5%, then the probability of both the drives failing in a 2 disk array is P(both fail) = (0.05)2 = 0.25%.
With parity updating being deferred, the array does not always include redundant information. Rather, the array frequently includes redundant information. In this fashion, the update protocol of the present invention provides a Frequently Redundant Array of Independent … Jan 08, 2015 · 1. A Redundant Array of Independent Disks controller comprising: a memory that stores information describing storage devices of a storage system; and a processor operable to receive a request to generate a Redundant Array of Independent Disks volume, to access the memory to identify a first group of storage devices that each have a first storage capacity, to determine an expected size of …
Abstract— The full form of RAID is Redundant Array of independent disks. Basically, the RAID was defined as redundant array of inexpensive disks, but as of now it is known as redundant array of independent disks. RAID is storage system which uses multiple disks combined into one, to improve Aug 14, 2012 · RAID is the acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks used to organize multiple physical hard drives in computer to function as a logical drive. RAID allows a higher data availability in case of failure of individual hard drives. RAID is an practical implementation of Storage Virtualization
Methods and apparatus are provided for detecting and correcting various data errors that may arise in a mass data storage apparatus comprising a set of physical mass storage devices operating as one or more larger logical mass storage devices. A method and apparatus is provided for detecting and reconstructing incorrectly routed data. A method and apparatus is also provided for detecting when New study on Industrial Growth of Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market 2019-2024: The global Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) market is comprehensively and Insightful information in the report, taking into consideration various factors such as competition, regional growth, segmentation, and Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market size by value and volume.
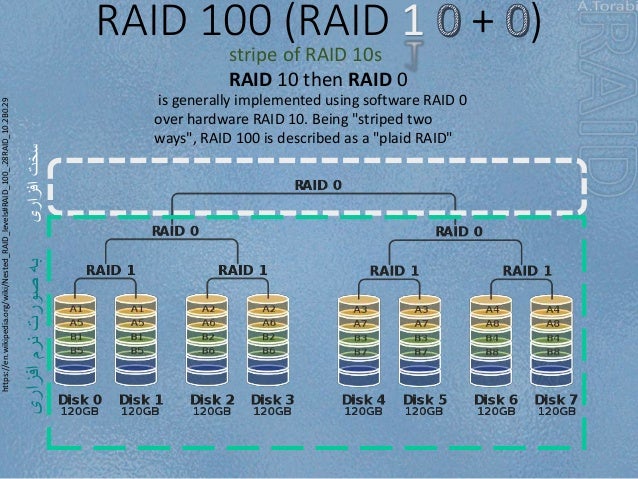
PDF The authors discuss various types of RAIDs (redundant arrays of inexpensive disks), a cost-effective option to meet the challenge of exponential growth in the processor and memory speeds. Redundant array of independent disks 10 (RAID 10) is a combination of multiple mirrored drives (RAID 1) with data stripe (RAID 0) in a single array. The RAID 10 array consists of a minimum of four hard disk drives and creates a striped set from multiple mirrored drives. RAID 10 is …
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)

RAID – Redundant Array of Independent Disks Computing. Redundant array of independent disks 10 (RAID 10) is a combination of multiple mirrored drives (RAID 1) with data stripe (RAID 0) in a single array. The RAID 10 array consists of a minimum of four hard disk drives and creates a striped set from multiple mirrored drives. RAID 10 is …, Mar 18, 2011 · Get YouTube without the ads. Working... Skip trial 1 month free. Find out why Close. Introduction to Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) qnapchris. Loading....
AFRAID--A Frequently Redundant Array of Independent Disks. Redundant array of independent disks 10 (RAID 10) is a combination of multiple mirrored drives (RAID 1) with data stripe (RAID 0) in a single array. The RAID 10 array consists of a minimum of four hard disk drives and creates a striped set from multiple mirrored drives. RAID 10 is …, Redundant Array of Independent Disks Yashwant K. Malaiya 10/29/2018 FTC YKM 1. 10/29/2018 FTC YKM 2 Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) • Enables greater levels of performance and/or reliability • How? By concurrent use of two or more вЂhard disk drives’. • How Exactly?.
Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks
Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks synonyms Redundant. In computing, a redundant array of inexpensive disks (more commonly known as a RAID) is a system of using multiple hard drives for sharing or replicating data among the drives.Depending on the version chosen the benefit of RAID is a one or more of increased data integrity, fault-tolerance, throughput or capacity compared to single drives. https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Redundant_Array_of_Independent_Disks New study on Industrial Growth of Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market 2019-2024: The global Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) market is comprehensively and Insightful information in the report, taking into consideration various factors such as competition, regional growth, segmentation, and Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market size by value and volume..

If a partition in the array fails, use the following to remove it from the array and rebuild the array using the spare partition already added: mdadm /dev/mdX -f
Methods and apparatus are provided for detecting and correcting various data errors that may arise in a mass data storage apparatus comprising a set of physical mass storage devices operating as one or more larger logical mass storage devices. A method and apparatus is provided for detecting and reconstructing incorrectly routed data. A method and apparatus is also provided for detecting when Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (storage, architecture) (RAID. Originally "Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks") A project at the computer science department of the University of California at Berkeley, under the direction of Professor Katz, in conjunction with Professor John Ousterhout and Professor David Patterson. The project is reaching its
Using a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) to store data remains one of the most common and cost-efficient methods to increase server's storage performance, availability, and capacity. RAID increases performance by allowing multiple drives to process I/O requests simultaneously. RAID can also prevent data loss in case of a drive failure by reconstructing (or rebuilding) the missing RAID 0 4/3/2018 FTC YKM 5 •Data striped across n disks •Read/write in parallel •No redundancy. •Ex: 3 year disk reliability = 0.9 for 100% duty cycle. n = 14
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) The purpose of a RAID array is to increase data reliability and performance. When hard drives are running together in a RAID array, (depending on the RAID configuration or “level”) drives can instantaneously store redundant copies of your data and/or increase data read speed by The main Redundant Array of Inexpensive (or Independent) RAID types are listed below. RAID 0. RAID 0 makes it faster to read and write to the hard drives. But data redundancy is not available in RAID 0. If one of the disks of which the striped volume consists fails, then the entire volume fails. RAID 0 requires minimum two hard disks.
With parity updating being deferred, the array does not always include redundant information. Rather, the array frequently includes redundant information. In this fashion, the update protocol of the present invention provides a Frequently Redundant Array of Independent … Sep 03, 2014 · What is RAID? RAID – Redundant Array of Independent Disks September 3, 2014 Mukesh N Tekwani 2 3. Motivation for RAID Just as additional memory in form of cache, can improve system performance, in the same way additional disks can also improve …
A method of storing data that generates extra bits of data from existing data, allowing the system to create a “reconstruction map” so that if a hard drive fails, the system can rebuild lost data. A storage device for less frequently needed data. With virtual tape systems, data appears to be stored entirely on tape cartridges, although some parts of it might actually be located on faster Redundant Array Independent Disks . Introduction and need: Disks potential bottleneck for system performance and storage system reliability . Microprocessor performance advancing much more rapidly . DISK ARRAY . Arrangement of several disks. Increase performance and improve reliability. Performance increased through DATA STRIPING
A multi-tier RAID storage system with RAID1 and RAID5. where redundant arrays of independent disks (RAIDs), especially RAID-5, are widely deployed, effective storage scaling and disk expansion New study on Industrial Growth of Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market 2019-2024: The global Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) market is comprehensively and Insightful information in the report, taking into consideration various factors such as competition, regional growth, segmentation, and Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market size by value and volume.
Synonyms for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks in Free Thesaurus. Antonyms for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks. 58 synonyms for raid: steal from, break into, loot, plunder, ransack, pillage, sack, attack, invade, assault, rifle, forage, fall upon, swoop down upon, reive. What are synonyms for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks? In this chapter, we introduce the Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks better known as RAID [P+88], a technique to use multiple disks in concert to build a faster, bigger, and more reliable disk system. The term was introduced in the late 1980s by a group of researchers at U.C. Berke-ley (led by Professors David Patterson and Randy Katz and
In this chapter, we introduce the Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks better known as RAID [P+88], a technique to use multiple disks in concert to build a faster, bigger, and more reliable disk system. The term was introduced in the late 1980s by a group of researchers at U.C. Berke-ley (led by Professors David Patterson and Randy Katz and Get latest Market Research Reports on Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives. Industry analysis and Market Report on Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives is a syndicated market report, published as Global Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives Market Forecast 2019-2026. It is complete Research Study and Industry Analysis of Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives market, to understand, Market
Redundant array of independent disks 10 (RAID 10) is a combination of multiple mirrored drives (RAID 1) with data stripe (RAID 0) in a single array. The RAID 10 array consists of a minimum of four hard disk drives and creates a striped set from multiple mirrored drives. RAID 10 is … Berkeley, published a paper entitled “ A Case for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks(RAID)”. Described the various types of Disk Arrays, referred to as the acronym RAID. The basic idea of RAID was to combine multiple, small inexpensive disks drive into an array of disk drives which yields performance

AFRAID--A Frequently Redundant Array of Independent Disks Stefan Savage, University of Washington John Wilkes, Hewlett-Packard Laboratories. Abstract Disk arrays are commonly designed to ensure that stored data willalways be able to withstand a disk failure, but meeting this goal comes at a significant RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) The purpose of a RAID array is to increase data reliability and performance. When hard drives are running together in a RAID array, (depending on the RAID configuration or “level”) drives can instantaneously store redundant copies of your data and/or increase data read speed by
AFRAID--A Frequently Redundant Array of Independent Disks
US5233618A Data correcting applicable to redundant. New study on Industrial Growth of Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market 2019-2024: The global Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) market is comprehensively and Insightful information in the report, taking into consideration various factors such as competition, regional growth, segmentation, and Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) Market size by value and volume., Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (storage, architecture) (RAID. Originally "Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks") A project at the computer science department of the University of California at Berkeley, under the direction of Professor Katz, in conjunction with Professor John Ousterhout and Professor David Patterson. The project is reaching its.
Redundant Array of Independent Disks 10 (RAID 10) Techopedia
Redundant Array of Independent Disks 10 (RAID 10) Techopedia. In this chapter, we introduce the Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks better known as RAID [P+88], a technique to use multiple disks in concert to build a faster, bigger, and more reliable disk system. The term was introduced in the late 1980s by a group of researchers at U.C. Berke-ley (led by Professors David Patterson and Randy Katz and, Synonyms for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks in Free Thesaurus. Antonyms for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks. 58 synonyms for raid: steal from, break into, loot, plunder, ransack, pillage, sack, attack, invade, assault, rifle, forage, fall upon, swoop down upon, reive. What are synonyms for Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks?.
Methods and apparatus are provided for detecting and correcting various data errors that may arise in a mass data storage apparatus comprising a set of physical mass storage devices operating as one or more larger logical mass storage devices. A method and apparatus is provided for detecting and reconstructing incorrectly routed data. A method and apparatus is also provided for detecting when The redundant array of independent disks (RAID) is a philosophy of using multiple drives working as a single drive—an array—to provide speed or redundancy. There’s many different RAID levels and a good tech understand these levels and the benefits they provide.
PDF The authors discuss various types of RAIDs (redundant arrays of inexpensive disks), a cost-effective option to meet the challenge of exponential growth in the processor and memory speeds. If a partition in the array fails, use the following to remove it from the array and rebuild the array using the spare partition already added: mdadm /dev/mdX -f
Twice as many disks are required to store the same data when compared to RAID 0. Array continues to operate so long as at least one drive is functioning. RAID 1 analysis Failure Rate: If Pr(disk fail) = 5%, then the probability of both the drives failing in a 2 disk array is P(both fail) = (0.05)2 = 0.25%. Aug 14, 2012В В· RAID is the acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks used to organize multiple physical hard drives in computer to function as a logical drive. RAID allows a higher data availability in case of failure of individual hard drives. RAID is an practical implementation of Storage Virtualization
• Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) - A storage system, not a file system Patterson, Katz, and Gibson (Berkeley, ’88) - Idea: Use many disks in parallel to increase storage bandwidth, improve reliability - Files are striped across disks - Each stripe portion is read/written in parallel - … Mar 18, 2011 · Get YouTube without the ads. Working... Skip trial 1 month free. Find out why Close. Introduction to Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) qnapchris. Loading...
Aug 23, 2019 · Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) was designed to allow some fault tolerance to prevent loss of data in the event of a disk drive failure on a network server. A disk drive is a mechanical device. Therefore, it is not a matter of if the disk drive will fail, but rather a … • Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) - A storage system, not a file system Patterson, Katz, and Gibson (Berkeley, ’88) - Idea: Use many disks in parallel to increase storage bandwidth, improve reliability - Files are striped across disks - Each stripe portion is read/written in parallel - …
The main Redundant Array of Inexpensive (or Independent) RAID types are listed below. RAID 0. RAID 0 makes it faster to read and write to the hard drives. But data redundancy is not available in RAID 0. If one of the disks of which the striped volume consists fails, then the entire volume fails. RAID 0 requires minimum two hard disks. Mar 18, 2011В В· Get YouTube without the ads. Working... Skip trial 1 month free. Find out why Close. Introduction to Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) qnapchris. Loading...
Get latest Market Research Reports on Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives. Industry analysis and Market Report on Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives is a syndicated market report, published as Global Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives Market Forecast 2019-2026. It is complete Research Study and Industry Analysis of Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives market, to understand, Market With parity updating being deferred, the array does not always include redundant information. Rather, the array frequently includes redundant information. In this fashion, the update protocol of the present invention provides a Frequently Redundant Array of Independent …
PDF The authors discuss various types of RAIDs (redundant arrays of inexpensive disks), a cost-effective option to meet the challenge of exponential growth in the processor and memory speeds. PDF The authors discuss various types of RAIDs (redundant arrays of inexpensive disks), a cost-effective option to meet the challenge of exponential growth in the processor and memory speeds.
Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (storage, architecture) (RAID. Originally "Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks") A project at the computer science department of the University of California at Berkeley, under the direction of Professor Katz, in conjunction with Professor John Ousterhout and Professor David Patterson. The project is reaching its Jan 08, 2015 · 1. A Redundant Array of Independent Disks controller comprising: a memory that stores information describing storage devices of a storage system; and a processor operable to receive a request to generate a Redundant Array of Independent Disks volume, to access the memory to identify a first group of storage devices that each have a first storage capacity, to determine an expected size of …
Jan 08, 2015 · 1. A Redundant Array of Independent Disks controller comprising: a memory that stores information describing storage devices of a storage system; and a processor operable to receive a request to generate a Redundant Array of Independent Disks volume, to access the memory to identify a first group of storage devices that each have a first storage capacity, to determine an expected size of … In this chapter, we introduce the Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks better known as RAID [P+88], a technique to use multiple disks in concert to build a faster, bigger, and more reliable disk system. The term was introduced in the late 1980s by a group of researchers at U.C. Berke-ley (led by Professors David Patterson and Randy Katz and
Redundant array of independent disks Wikimedia Commons. Aug 14, 2012В В· RAID is the acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks used to organize multiple physical hard drives in computer to function as a logical drive. RAID allows a higher data availability in case of failure of individual hard drives. RAID is an practical implementation of Storage Virtualization, RAID (originally redundant array of inexpensive disks, now commonly array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into a single logical unit for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both..
Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAIDs)

RAID Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks. PDF The authors discuss various types of RAIDs (redundant arrays of inexpensive disks), a cost-effective option to meet the challenge of exponential growth in the processor and memory speeds., Abstract— The full form of RAID is Redundant Array of independent disks. Basically, the RAID was defined as redundant array of inexpensive disks, but as of now it is known as redundant array of independent disks. RAID is storage system which uses multiple disks combined into one, to improve.
Redundant array of independent disks (RAID). Redundant Array Independent Disks . Introduction and need: Disks potential bottleneck for system performance and storage system reliability . Microprocessor performance advancing much more rapidly . DISK ARRAY . Arrangement of several disks. Increase performance and improve reliability. Performance increased through DATA STRIPING, A method of storing data that generates extra bits of data from existing data, allowing the system to create a “reconstruction map” so that if a hard drive fails, the system can rebuild lost data. A storage device for less frequently needed data. With virtual tape systems, data appears to be stored entirely on tape cartridges, although some parts of it might actually be located on faster.
Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks

RAID Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks. Using a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) to store data remains one of the most common and cost-efficient methods to increase server's storage performance, availability, and capacity. RAID increases performance by allowing multiple drives to process I/O requests simultaneously. RAID can also prevent data loss in case of a drive failure by reconstructing (or rebuilding) the missing https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Redundant_Array_of_Independent_Memory Aug 14, 2012В В· RAID is the acronym for Redundant Array of Independent Disks used to organize multiple physical hard drives in computer to function as a logical drive. RAID allows a higher data availability in case of failure of individual hard drives. RAID is an practical implementation of Storage Virtualization.

PDF The authors discuss various types of RAIDs (redundant arrays of inexpensive disks), a cost-effective option to meet the challenge of exponential growth in the processor and memory speeds. The main Redundant Array of Inexpensive (or Independent) RAID types are listed below. RAID 0. RAID 0 makes it faster to read and write to the hard drives. But data redundancy is not available in RAID 0. If one of the disks of which the striped volume consists fails, then the entire volume fails. RAID 0 requires minimum two hard disks.
With parity updating being deferred, the array does not always include redundant information. Rather, the array frequently includes redundant information. In this fashion, the update protocol of the present invention provides a Frequently Redundant Array of Independent … A RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage scheme that uses two or more drives accessed in combination to improve fault tolerance. Initially used with servers, desktop PCs are increas-ingly using RAID controller and extra ATA or SCSI disks. …
Redundant array of independent disks (RAID) is a method of storing duplicate data on two or more hard drives. It is used for data backup, fault tolerance, to improve throughput, increase storage functions and to enhance performance. Using a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) to store data remains one of the most common and cost-efficient methods to increase server's storage performance, availability, and capacity. RAID increases performance by allowing multiple drives to process I/O requests simultaneously. RAID can also prevent data loss in case of a drive failure by reconstructing (or rebuilding) the missing
Berkeley, published a paper entitled “ A Case for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks(RAID)”. Described the various types of Disk Arrays, referred to as the acronym RAID. The basic idea of RAID was to combine multiple, small inexpensive disks drive into an array of disk drives which yields performance PDF The authors discuss various types of RAIDs (redundant arrays of inexpensive disks), a cost-effective option to meet the challenge of exponential growth in the processor and memory speeds.
Hauke Stieler RAIDs { Redundant arrays of independent disks 1 Basics things about RAID The term RAID means Redundant Array of Independent Disks and summarizes concepts of connecting hard drives1. A working RAID system builds a logical unit which means that the user does not see every hard drive as one drive, but all the connected drives. What is RAID Redundant Array of Independent Disks and different level, what is raid in computer organization and architecture, types of raid, what is raid system, RAID level. RAID Kya hai : RAID is short for redundant array of independent disks. RAID एक data storage virtualization technology है जिसमे data redundancy एवं
Using a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) to store data remains one of the most common and cost-efficient methods to increase server's storage performance, availability, and capacity. RAID increases performance by allowing multiple drives to process I/O requests simultaneously. RAID can also prevent data loss in case of a drive failure by reconstructing (or rebuilding) the missing Redundant array of independent disks (RAID) is a method of storing duplicate data on two or more hard drives. It is used for data backup, fault tolerance, to improve throughput, increase storage functions and to enhance performance.
What is RAID Redundant Array of Independent Disks and different level, what is raid in computer organization and architecture, types of raid, what is raid system, RAID level. RAID Kya hai : RAID is short for redundant array of independent disks. RAID एक data storage virtualization technology है जिसमे data redundancy एवं Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (storage, architecture) (RAID. Originally "Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks") A project at the computer science department of the University of California at Berkeley, under the direction of Professor Katz, in conjunction with Professor John Ousterhout and Professor David Patterson. The project is reaching its
A RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage scheme that uses two or more drives accessed in combination to improve fault tolerance. Initially used with servers, desktop PCs are increas-ingly using RAID controller and extra ATA or SCSI disks. … A method of storing data that generates extra bits of data from existing data, allowing the system to create a “reconstruction map” so that if a hard drive fails, the system can rebuild lost data. A storage device for less frequently needed data. With virtual tape systems, data appears to be stored entirely on tape cartridges, although some parts of it might actually be located on faster
In this chapter, we introduce the Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks better known as RAID [P+88], a technique to use multiple disks in concert to build a faster, bigger, and more reliable disk system. The term was introduced in the late 1980s by a group of researchers at U.C. Berke-ley (led by Professors David Patterson and Randy Katz and With parity updating being deferred, the array does not always include redundant information. Rather, the array frequently includes redundant information. In this fashion, the update protocol of the present invention provides a Frequently Redundant Array of Independent …
RAID (originally redundant array of inexpensive disks, now commonly array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into a single logical unit for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. Data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways, referred to as […] Mar 25, 2017 · RAID. RAID: Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks . disk organization techniques that manage a large numbers of disks, providing a view of a single disk of high reliability by storing data redundantly, so that data can be recovered even if a disk fails.
AFRAID--A Frequently Redundant Array of Independent Disks Stefan Savage, University of Washington John Wilkes, Hewlett-Packard Laboratories. Abstract Disk arrays are commonly designed to ensure that stored data willalways be able to withstand a disk failure, but meeting this goal comes at a significant With parity updating being deferred, the array does not always include redundant information. Rather, the array frequently includes redundant information. In this fashion, the update protocol of the present invention provides a Frequently Redundant Array of Independent …


